OSI Model & TCP/IP Reference
Mô hình OSI & TCP/IP Reference
A complete guide to the 7 network layers, mapping, and security.
Hướng dẫn đầy đủ về 7 tầng mạng, ánh xạ và bảo mật.
Explore Now Khám phá ngayI. OSI Model vs TCP/IP Mapping I. Ánh xạ Mô hình OSI và TCP/IP
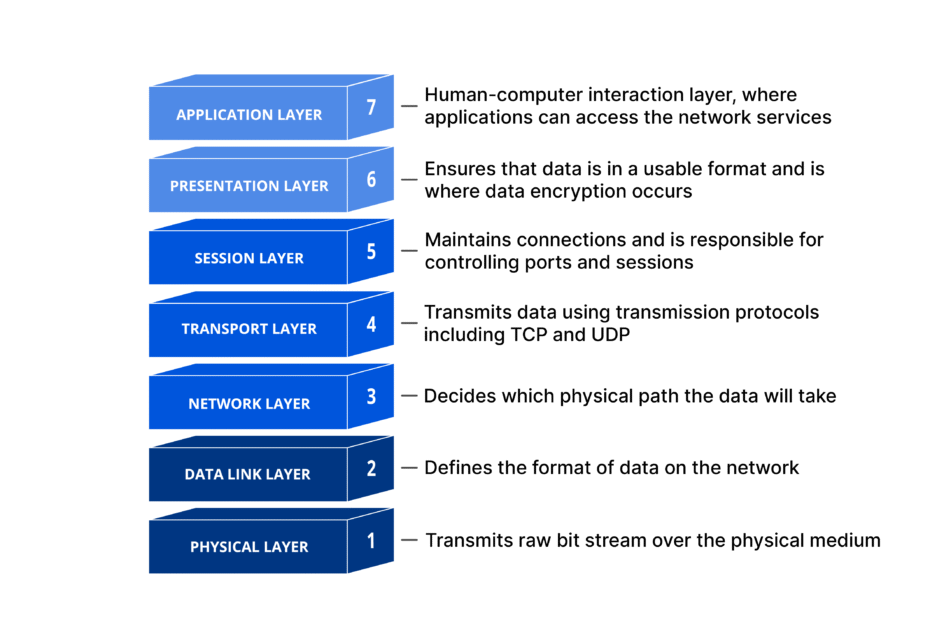
OSI is a 7-layer theoretical model. TCP/IP is a 4-layer practical implementation.
OSI là mô hình lý thuyết 7 tầng. TCP/IP là triển khai thực tế 4 tầng.
| OSI LayerTầng OSI | TCP/IP LayerTầng TCP/IP | Key Protocols & FunctionGiao thức & Chức năng |
|---|---|---|
| 7. Application7. Ứng dụng | ApplicationỨng dụng |
Protocols: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS, SSH. Function: End-user application services. Giao thức: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS, SSH. Chức năng: Dịch vụ ứng dụng người dùng. |
| 6. Presentation6. Trình diễn | ||
| 5. Session5. Phiên | ||
| 4. Transport4. Giao vận | TransportGiao vận |
Protocols: TCP, UDP. Function: End-to-end delivery and reliability. Giao thức: TCP, UDP. Chức năng: Giao nhận đầu-cuối & tin cậy. |
| 3. Network3. Mạng | InternetMạng Internet |
Protocols: IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, ARP, IPsec. Function: Logical addressing and routing. Giao thức: IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, ARP, IPsec. Chức năng: Địa chỉ logic & định tuyến. |
| 2. Data Link2. Liên kết | Network AccessTruy cập mạng |
Protocols: Ethernet, Wi-Fi, PPP, ARP. Function: Physical transmission and local delivery. Giao thức: Ethernet, Wi-Fi, PPP, ARP. Chức năng: Truyền dẫn vật lý & nội bộ. |
| 1. Physical1. Vật lý |
II. Layer 7: Application II. Tầng 7: Ứng dụng
DATAProvides network services directly to end-user applications. Acts as the interface between software and network protocols, enabling applications to access and utilize network resources.
Cung cấp các dịch vụ mạng trực tiếp cho ứng dụng người dùng cuối. Đóng vai trò là giao diện giữa phần mềm và giao thức mạng.
HTTP/HTTPS (Web browsing) • FTP/SFTP (File transfer) • SMTP/IMAP/POP3 (Email) • DNS (Name resolution) • SSH (Secure shell) • SNMP (Network management) • Telnet (Remote access)
DNS resolution failures, HTTP 404/500 errors, Email delivery problems, Application timeouts, Certificate errors (HTTPS), Authentication failures
Lỗi phân giải DNS, mã lỗi HTTP 404/500, lỗi gửi email, hết hạn phiên ứng dụng, lỗi chứng chỉ SSL (HTTPS), lỗi xác thực.
III. Layer 6: Presentation III. Tầng 6: Trình diễn
DATAData translation, encryption, and compression. Ensures different systems can communicate by converting data formats and handling syntax differences.
Dịch định dạng dữ liệu, mã hóa và nén. Đảm bảo các hệ thống khác nhau có thể giao tiếp bằng cách chuyển đổi định dạng và xử lý sự khác biệt cú pháp.
- Character Encoding:Mã hóa ký tự: ASCII, Unicode, EBCDIC conversion
- Data Compression:Nén dữ liệu: JPEG, MPEG, GIF compression
- Encryption/Decryption:Mã hóa/Giải mã: SSL/TLS, AES, RSA
- Format Conversion:Chuyển đổi định dạng: MIME, XDR
IV. Layer 5: Session IV. Tầng 5: Phiên
DATAEstablishes, manages, and terminates communication sessions. Handles dialog control and synchronization between applications.
Thiết lập, quản lý và kết thúc các phiên liên lạc giữa các ứng dụng. Phụ trách điều khiển hội thoại và đồng bộ hóa.
NetBIOS • RPC • SOCKS • PPTP • L2TP • Session management APIs
Session hijacking, Session fixation, Man-in-the-middle attacks, CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery)
Cướp quyền điều khiển phiên (Hijacking), Giả mạo phiên, Tấn công xen giữa (MITM), CSRF.
V. Layer 4: Transport V. Tầng 4: Giao vận
SEGMENTProvides end-to-end communication. Key functions include:
Cung cấp giao tiếp đầu-cuối. Các chức năng chính bao gồm:
- Error Recovery: Ensures data arrives reliably (e.g., TCP’s acknowledgments).Phục hồi lỗi: Đảm bảo dữ liệu đến đích tin cậy (ví dụ: các xác nhận ACK của TCP).
- Flow Control: An adaptive mechanism that matches the sender’s sending speed to the receiver’s processing speed.Kiểm soát luồng: Khớp tốc độ bên gửi với khả năng xử lý của bên nhận.
- Multiplexing: Uses port numbers to direct data segments to the correct application.Ghép kênh: Dùng số hiệu cổng điều phối dữ liệu cho đúng ứng dụng.
| Feature | Đặc điểm | TCP (Transmission Control) | UDP (User Datagram) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConnectionKết nối | Connection-oriented (3-way handshake)Hướng kết nối (Handshake 3 bước) | Connectionless (no handshake)Không kết nối (Không handshake) | |
| ReliabilityĐộ tin cậy | Reliable (ACK, retransmission, ordering)Tin cậy (ACK, gửi lại, thứ tự gói tin) | Unreliable (best effort, no guarantees)Không tin cậy (nỗ lực tối đa, không đảm bảo) | |
| SpeedTốc độ | Slower (overhead for reliability)Chậm hơn (do overhead kiểm tra tin cậy) | Faster (minimal overhead)Nhanh hơn (overhead tối thiểu) | |
| Header SizeKích thước Header | 20 – 60 bytes | 8 bytes | |
| Use CasesTrường hợp sử dụng | Web (HTTP/HTTPS), Email, File transferWeb (HTTP/HTTPS), Email, Truyền tệp | Streaming, Gaming, VoIP, DNSStreaming, Trò chơi, VoIP, DNS |
VI. Layer 3: Network VI. Tầng 3: Mạng
PACKETLogical addressing (IP) and routing. Determines optimal path for packets across multiple networks from source to destination.
Địa chỉ logic (IP) và định tuyến. Xác định đường đi tối ưu cho các gói tin qua nhiều mạng từ nguồn đến đích.
IPv4: 32-bit (e.g., 192.168.1.1), ~4.3B addresses, dotted decimal
IPv6: 128-bit (e.g., 2001:db8::1), ~3.4×10³⁸ addresses, hexadecimal
Private Ranges: 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16
Special: 127.0.0.1 (loopback), .0 (network), .255 (broadcast)
Static: Manual routes • Dynamic IGP: OSPF, RIP, EIGRP • Dynamic EGP: BGP • Other: ICMP (ping/traceroute), IGMP (multicast), IPsec (VPN).
VII. Layer 2: Data Link VII. Tầng 2: Liên kết dữ liệu
FRAMENode-to-node delivery within the same local network. Handles framing, physical addressing (MAC), error detection, and flow control.
Chuyển phát dữ liệu giữa các nút trong cùng một mạng nội bộ. Xử lý đóng khung (framing), địa chỉ vật lý (MAC), phát hiện lỗi và kiểm soát luồng.
MAC Address (Layer 2):Địa chỉ MAC (Tầng 2):
- 48-bit hardware address (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E)Địa chỉ phần cứng 48-bit (ví dụ: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E)
- Burned into NIC, unique per deviceĐược gắn cứng vào card mạng, duy nhất cho mỗi thiết bị
- Local network scope onlyChỉ có giá trị trong phạm vi mạng nội bộ
- Format: OUI (first 3 bytes) + Device ID (last 3 bytes)Định dạng: OUI (3 byte đầu) + ID thiết bị (3 byte cuối)
IP Address (Layer 3):Địa chỉ IP (Tầng 3):
- 32/128-bit logical addressĐịa chỉ logic 32/128-bit
- Assigned via DHCP or static configĐược cấp qua DHCP hoặc cấu hình tĩnh
- Global routing scopePhạm vi định tuyến toàn cầu
- Can change based on network locationCó thể thay đổi tùy theo vị trí mạng kết nối
Switch (Layer 2):Switch (Tầng 2): Uses MAC addresses, forwards frames within LAN, creates collision domains.Sử dụng địa chỉ MAC, chuyển tiếp khung trong LAN, tạo ra các miền xung đột (collision domains).
Router (Layer 3):Router (Tầng 3): Uses IP addresses, routes packets between networks, connects LANs/WANs.Sử dụng địa chỉ IP, định tuyến gói tin giữa các mạng, kết nối các mạng LAN/WAN với nhau.
📡 Protocols & Devices: Ethernet (802.3), Wi-Fi (802.11), PPP, ARP, VLAN (802.1Q) • Devices: Switches, Bridges, NICs
VIII. Layer 1: Physical VIII. Tầng 1: Vật lý
BITPhysical transmission of raw bit streams. Defines electrical, mechanical, and procedural specifications for activating and maintaining physical links.
Truyền dẫn vật lý các luồng bit thô. Định nghĩa các đặc tính kỹ thuật về điện, cơ và quy trình để kích hoạt và duy trì các liên kết vật lý.
| Copper | Cat5e/6/6a (1/10Gbps), Coaxial |
| Fiber | Single-mode (long distance), Multi-mode, DWDM |
| Wireless | 802.11ac/ax (Wi-Fi 5/6), Bluetooth, NFC |
| Standards | 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T, 10GBASE-T |
Cables, Hubs, Repeaters, Transceivers, NICs • Tools: Cable testers, OTDR, Tone generators.
IX. How Data Encapsulation Works (Sending) IX. Cơ chế Đóng gói Dữ liệu (Khi gửi đi)
X. Key Concepts ReviewX. Tổng ôn kiến thức
| ConceptKhái niệm | DescriptionMô tả | Layer |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address | Logical, unique address for a device on a network (e.g., 192.168.1.10). Can change.Địa chỉ logic, duy nhất cho một thiết bị trên mạng (vd: 192.168.1.10). Có thể thay đổi. | Layer 3 |
| MAC Address | Physical, globally unique hardware address burned into the network card (e.g., 0A:2B:C3:4D:5E:6F). Does not change.Địa chỉ vật lý, duy nhất toàn cầu được gắn cứng trên card mạng (vd: 0A:2B:C3:4D:5E:6F). Không thay đổi. | Layer 2 |
| Router | A device that connects different networks and forwards packets between them based on IP addresses.Thiết bị kết nối các mạng khác nhau và chuyển tiếp gói tin dựa trên địa chỉ IP. | Layer 3 |
| Switch | A device that connects devices on a *local* network and forwards frames between them based on MAC addresses.Thiết bị kết nối các thiết bị trong mạng *nội bộ* và chuyển tiếp khung (frame) dựa trên địa chỉ MAC. | Layer 2 |
| Hub | An old “dumb” device that just repeats all traffic to all ports. Creates collisions.Thiết bị cũ “ngu ngơ” chỉ lặp lại mọi traffic ra tất cả các cổng. Dễ gây xung đột (collision). | Layer 1 |
| Port | A number used at the Transport layer to identify a specific application or service on a device.Một con số ở tầng Giao vận dùng để xác định một ứng dụng hoặc dịch vụ cụ thể trên thiết bị. | Layer 4 |
Quick Comparison: Q&AHỏi & Đáp nhanh
A quick reference table for common comparison questions to help reinforce key concepts from the article.
Bảng tra cứu nhanh cho các câu hỏi so sánh phổ biến để giúp củng cố kiến thức trong bài viết.
| QuestionCâu hỏi | Quick Answer (Key Difference)Đáp án nhanh (Sự khác biệt chính) | Layer |
|---|---|---|
| How do TCP and UDP differ?TCP và UDP khác nhau thế nào? | TCP: Reliable, connection-oriented (3-way handshake). UDP: Unreliable, connectionless (send and forget).TCP: Tin cậy, hướng kết nối (handshake 3 bước). UDP: Không tin cậy, không kết nối (gửi và quên). |
Layer 4 |
| What’s the difference between a MAC and IP address?Sự khác biệt giữa MAC và IP? | MAC: Physical, fixed address used within a LAN. IP: Logical, changeable address used for global routing.MAC: Địa chỉ vật lý, cố định trong mạng LAN. IP: Địa chỉ logic, có thể thay đổi dùng để định tuyến toàn cầu. |
L2 / L3 |
| What’s the difference between a Switch and a Router?Sự khác biệt giữa Switch và Router? | Switch: Uses MAC addresses to forward frames within one LAN. Router: Uses IP addresses to route packets between different networks.Switch: Dùng địa chỉ MAC để chuyển khung trong một LAN. Router: Dùng địa chỉ IP để định tuyến gói tin giữa các mạng khác nhau. |
L2 / L3 |
| Why does DNS use both TCP and UDP?Tại sao DNS dùng cả TCP và UDP? | UDP (Port 53): Standard queries (fast). TCP (Port 53): Zone transfers or large responses (reliable).UDP (Cổng 53): Truy vấn tiêu chuẩn (nhanh). TCP (Cổng 53): Truyền vùng (zone transfer) hoặc phản hồi lớn (tin cậy). |
L7 / L4 |
| What is the TCP 3-Way Handshake?Cơ chế TCP 3-Way Handshake là gì? | A 3-step process to establish a connection: (1) SYN, (2) SYN-ACK, (3) ACK.Quy trình 3 bước thiết lập kết nối: (1) SYN, (2) SYN-ACK, (3) ACK. | Layer 4 |
| Why FTP uses two ports (20 & 21)?Tại sao FTP dùng 2 cổng (20 & 21)? | Port 21 (Control): Sends commands and authentication. Port 20 (Data): Transmits the actual file data.Cổng 21 (Điều khiển): Gửi lệnh và xác thực. Cổng 20 (Dữ liệu): Truyền dữ liệu tệp thực tế. |
L7 / L4 |
XI. Security & Appendix XI. Bảo mật & Phụ lục
Common Security Threats by LayerMối đe dọa bảo mật theo tầng
🛡️ Defense in Depth
- Layer 7 Defense: Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Layer 4 Defense: Firewalls (blocking unused ports)
- Layer 3 Defense: Access Control Lists (ACLs) on routers
- Layer 2 Defense: Port Security on switches
Well-Known Ports (0-1023)Cổng mạng phổ biến (0-1023)
| Port | Proto | DescriptionMô tả | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20/21 | TCP | FTP – File Transfer (P20: Data, P21: Control). | Insecure |
| 22 | TCP | SSH – Secure Shell access to a server. | Secure |
| 23 | TCP | Telnet – Unencrypted CLI access. HIGHLY INSECURE. | Insecure |
| 25 | TCP | SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. | Caution |
| 53 | UDP/TCP | DNS – Domain Name translation. | Essential |
| 80 | TCP | HTTP – Standard unencrypted web traffic. | Insecure |
| 443 | TCP | HTTPS – Secure web traffic (SSL/TLS encrypted). | Secure |
| 3389 | TCP | RDP – Remote Desktop Protocol for Windows. | High-target |
• Principle of Least Privilege: Only open necessary ports.
• Avoid Insecure Protocols: Use SSH/SFTP over Telnet/FTP.
• Change Defaults: Don’t use standard ports for remote access.
• Nguyên tắc đặc quyền tối thiểu: Chỉ mở những cổng thực sự cần thiết.
• Giao thức an toàn: Dùng SSH/SFTP thay cho Telnet/FTP.
• Thay đổi mặc định: Tránh dùng cổng mặc định cho dịch vụ.
Troubleshooting MatrixMa trận xử lý sự cố OSI
| Layer | ProblemSự cố | QuestionCâu hỏi | Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Phys | Cable bad/unplugged | “Is it plugged in?” | Tester |
| 2. Data | MAC conflict, VLAN error | “Switch active?” | arp -a |
| 3. Net | Wrong IP, No gateway | “Can I ping 8.8.8.8?” | ping |
| 4. Trans | Firewall blocking Port | “Reach site on 80 not 443?” | telnet |
| 5-7. App | Auth error, DNS fail | “Brows Google works?” | Browser |
• Bottom-Up: Start at L1 confirmed before moving up.
• Top-Down: Start at L7 to check app issues first.
• Từ dưới lên (Bottom-Up): Bắt đầu từ Tầng 1 (Lỗi phần cứng).
• Từ trên xuống (Top-Down): Bắt đầu từ Tầng 7 (Lỗi phần mềm).